现成的WEB路径扫描工具颇多,但都不尽如人意,主要是它是根据返回的状态码来判断页面是否存在的,比如返回200,就认为找到页面,404则认为页面不存在。但这里有个问题,返回的状态码是服务端可控的,而工具对于状态码的判断规则大都是定死了的,这就使得扫描结果没有多大价值。
所以抽空写了个web扫描工具,它的原理是先探测一个肯定不存在的路径和页面,/mustnotexistspath/和/mustnotexistspath+ext ,将他两的返回码作为页面不存在的标志,如果与之不同,则页面可能存在,原理相当简单,起到了动态判断的效果。
代码为:
#!/usr/bin/python import httplib2
import sys if len(sys.argv) < 3: print(“written by lanz….”) print( “Usage: ” + sys.argv[0] + ” host ” + ” .ext”) print (“Eg: ” + sys.argv[0] + ” http://www.baidu.com .php”) sys.exit(0)
host = sys.argv[1] ext = sys.argv[2]
print(host)
http = httplib2.Http(“.cache”) response,content = http.request(host)
response,content=http.request(host+”/mustnotexistspath/”) nonpathstatus = response.status
response,content=http.request(host+”/mustnotexistspath”+ext) nonpathextstatus = response.status print(“NoneExistPathStatus:”,nonpathstatus) print(“NoneExistFileStatus:”,nonpathextstatus) f = open ( ‘WebPath.txt’, ‘r’ ) fileList = f.readlines()
def subscan(subpath): for fileLine in fileList: newline = fileLine.strip() path = subpath+”/”+newline response,content= http.request(path,”GET”) if response.status!=nonpathstatus: st = str(response.status) print(st+” : “+path) subscan(path) pathext=path + ext response,content= http.request(pathext,”GET”) if response.status!=nonpathextstatus: st = str(response.status) print(st+” : “+pathext)
subscan(host) f.close()
效果对比:
使用webtools扫描目录的结果图:
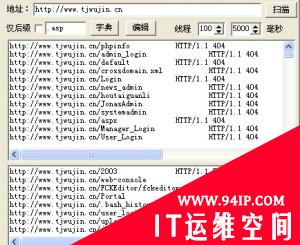
使用新代码得到的效果:
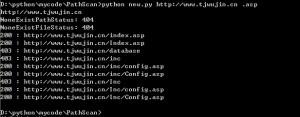
转载请注明:IT运维空间 » 安全防护 » python写的web路径扫描工具
















发表评论